Velocity-based training (VBT) has become a game-changer in safely and effectively training athletes, offering a data-driven approach to building strength and power.
Let’s check out everything you need to learn what velocity-based training is, including why it’s important, what devices you can use for it, and how it can revolutionize your current training.
What Is Velocity-Based Training?
Velocity-based training is a method of strength training that uses the speed of movement to determine the most optimal load for exercises.
Unlike classic strength training, which generally uses percentage-based loads or predetermined weights and repetitions, VBT focuses on the velocity at which an athlete can move a given load.
This lets us make immediate adjustments to training loads, so that our athletes are working at their most effective intensity levels—even if their performance is lower or higher than usual in a given training session.
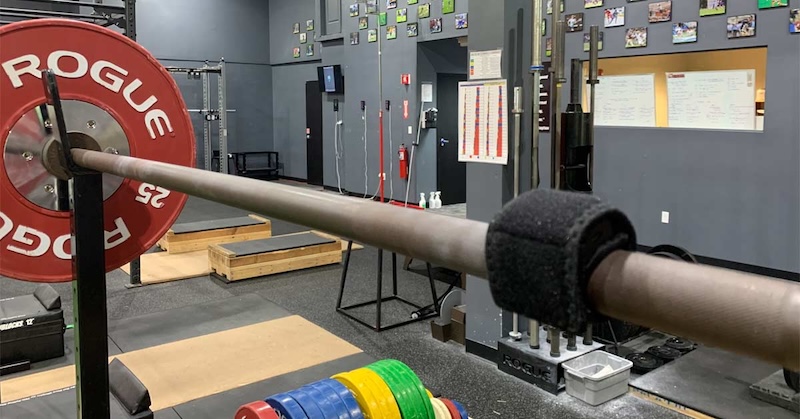

Image 1. The Enode sensor strapped to a barbell.
VBT is grounded in the principle that the speed of movement is directly related to the load being lifted.
By measuring the lift speed, we as coaches and trainers gain valuable insights into an athlete’s:
- Current performance
- Fatigue levels
- Readiness to train
By using the data, each training session is more personalized and effective while reducing the risk of overtraining and injury.
Key Components of VBT
There are three key components of velocity-based training:
- Velocity Zones: Different velocity zones match up to specific training outcomes like strength, power, or speed.
- Real-Time Feedback: Immediate data on movement speed helps make on-the-spot adjustments to training loads.
- Load-Velocity Profiling: Establishes a relationship between load and velocity to predict max strength capabilities (1RM) in a safe and accurate way.
Why Is Velocity-Based Training Important?
VBT has some big advantages that make it an important tool for athletic training.
1. Personalized Training
Every athlete is unique, and VBT allows for highly individualized training programs.
By measuring an athlete’s movement speed, coaches can tailor workouts to match the athlete’s current abilities and goals.
This means that training intensity lowers when the athlete is more fatigued, and rises when the athlete’s performance is optimal that session.
Athletes are always training at the proper intensity thanks to this personalized approach, which leads to better gains.
2. Real-Time Feedback
One of the biggest advantages of VBT is the ability to provide real-time feedback.
Athletes can see their performance metrics instantly, allowing them to make adjustments to their technique or exercise weight right aways.
This real-time feedback leads to more effective training sessions and faster progress.
3. Injury Prevention
By tracking movement speed, VBT helps identify signs of fatigue and overtraining—before they lead to injury!
Coaches can adjust training loads based on the VBT metrics to make sure that their athletes are not pushing past their limits, which reduces the risk of injury and overtraining.
4. Objective Data
VBT provides quantifiable data that can be tracked over time.
This helps set realistic benchmarks, track progress, and make informed decisions about training adjustments.
Plus, it can help motivate athletes as they have hard numbers to compare their performance to, allowing them to constantly compete against themselves.
Load-Velocity Profiling & Predicting 1RM
Load-velocity profiling involves plotting the relationship between different loads and the speeds at which they are lifted.
This predicts an athlete’s one-repetition maximum (1RM) without maximal lifts, which can be risky and taxing—especially if the athlete isn’t used to maximum effort lifts.
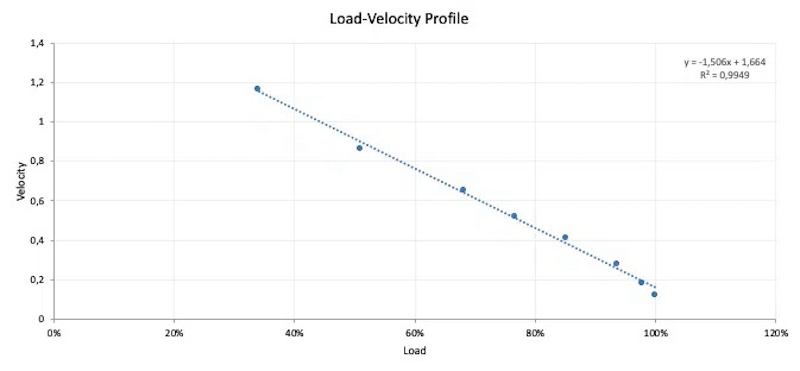
Figure 1. A basic Load-Velocity Profile (Via Vitruve).
Creating a Load-Velocity Profile
To create a load-velocity profile, athletes perform several lifts of the same exercise at different loads while their movement speed is measured.
That data is then mapped out on a graph, with load on the x-axis and velocity on the y-axis.
The resulting curve or line provides a visual representation of the relationship between load and velocity for that athlete.
This can be boiled down to a 3-step process:
- Data Collection: Measure the speed of lifts at several submaximal loads.
- Plotting the Curve: Create a graph plotting load against velocity.
- Extrapolation: Use the trend to predict the 1RM by identifying the load at which the velocity would approach 0.
Predicting 1RM with Load-Velocity Profiles
Once a load-velocity profile is established, it can be used to predict the athlete’s 1RM.
This is done by identifying the point where the velocity approaches zero, which would be the athlete’s max effort lift.
A traditional 1RM requires skill in whatever exercise is being tested, but it’s a skill that not every athlete has…
So, traditional 1RM testing is less accurate if the athlete hasn’t done a good amount of max lifts to the point that they’re comfortable with them, whereas everyone can do VBT.
And, VBT training is just as effective as traditional 1RM percentage-based training.
Benefits of Predicting 1RM with Load-Velocity Profiles
Predicting 1RM with load-velocity profiles offers some important benefits:
- Safety: Reduces the risks found with maximal lifts.
- Efficiency: Saves time and energy by avoiding frequent maximal testing, as well as the time required for athletes to become comfortable with max lifts.
- Accuracy: Provides a reliable estimate of strength.
Velocity Based Training Devices
Velocity Based Training is possible with specialized devices used to measure the speed of movement during lifts.
Here are two great VBT devices (all available at SimpliFaster):
Enode Pro
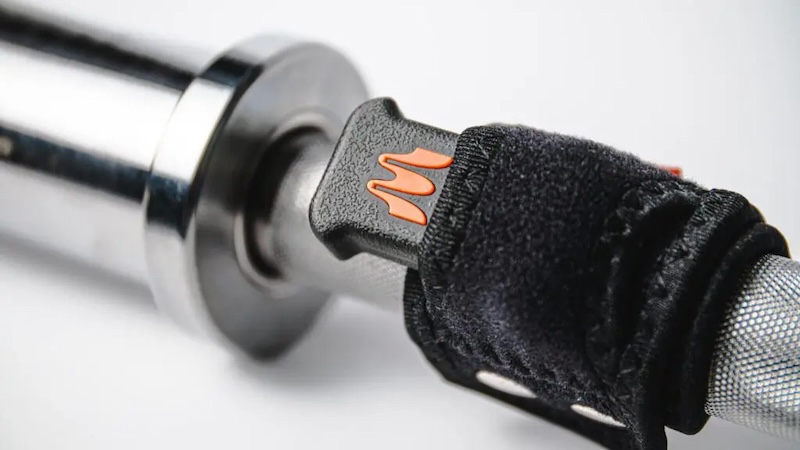

Image 2. The Enode Pro.
The Enode Pro is a wireless sensor that captures motion in 3 dimensions. It gives you quick measurements of power, velocity, duration, and more.
It’s perfect for velocity-based training with cleans, bench press, squats, jump training, deadlifts—the list goes on!
The Enode Pro is a more budget-friendly option than the device below, but it doesn’t skimp on quality!
GymAware Powertool
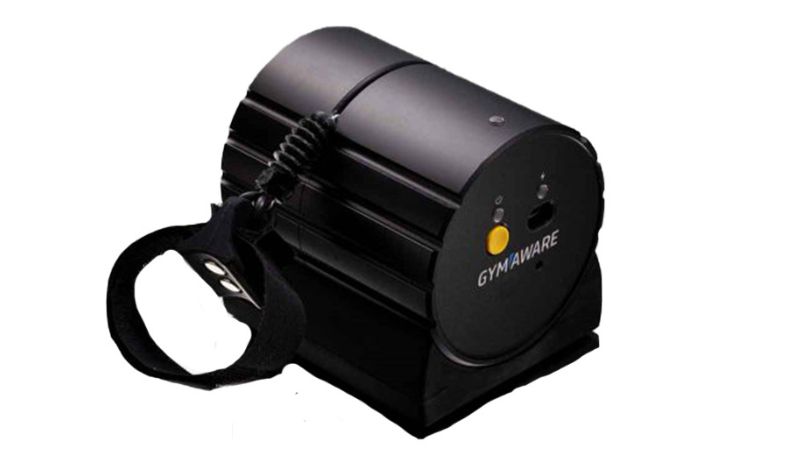

Image 3. The GymAware Powertool
The GymAware Powertool is a leading VBT device known for its accuracy and reliability.
It uses a sensor to measure bar speed and provides detailed data analysis through its app.
GymAware is widely used by elite sports teams and organizations for its high performance and user-friendly interface, often being called “the gold standard of velocity-based training.”
It has different kit options, letting you customize to your needs!
Final Thoughts
Velocity-based training represents a big step forward in athletic training, providing a data-driven approach to optimize performance, reduce injury risks, and personalize workouts.
Understanding what velocity-based training is can make your own or your athletes’ training routines that much more effective.
At SimpliFaster, we are committed to offering the best tools and resources to help you leverage the power of VBT.
With the right VBT devices and a data-driven approach, the potential for athletic development is limitless.
Explore our range of VBT devices and start your velocity-based training journey today!
FAQs
What is velocity-based training?
Velocity-based training is a training method that uses the speed of movement to determine the load and intensity of an exercise.
How does velocity-based training work?
Velocity-based training involves the use of specialized equipment to measure the speed of an athlete’s lift. This data is then used to adjust the training load and volume to make sure that the athlete is working within the optimal velocity zones for their specific training goals.
What are the benefits of velocity-based training?
VBT offers many benefits, including more precise load adjustments, improved performance tracking, increased athlete motivation, and reduced risk of overtraining and injuries.
What equipment is needed for velocity-based training?
SimpliFaster offers a selection of high-quality gear for your own velocity-based training that can accurately track the speed of your lifts.
How do you determine the optimal velocity zones for training?
Optimal velocity zones are typically determined based on the athlete’s specific training goals and the type of exercise being performed. Common velocity zones include strength-speed, speed-strength, and explosive strength.
Can velocity-based training prevent injuries?
By providing real-time feedback, VBT helps athletes avoid excessive strain and overtraining.
How does velocity-based training compare to traditional training methods?
VBT offers a more dynamic and responsive approach to training compared to traditional methods that rely on fixed percentages of one-rep max (1RM). VBT adjusts training loads in real-time based on the athlete’s performance, making it more adaptable to daily variations in strength and fatigue.
What is an example of velocity in exercise?
An example of velocity in exercise is measuring the speed at which an athlete performs a squat. Using a velocity measurement device, the speed of the lift is recorded, and the training load is adjusted based on the desired velocity zone, such as strength-speed or speed-strength.
What are the speed zones for velocity-based training?
Common zones are strength-speed (slow velocities with heavy loads), speed-strength (moderate velocities with moderate loads), and explosive strength (high velocities with lighter loads).
Since you’re here…
…we have a small favor to ask. More people are reading SimpliFaster than ever, and each week we bring you compelling content from coaches, sport scientists, and physiotherapists who are devoted to building better athletes. Please take a moment to share the articles on social media, engage the authors with questions and comments below, and link to articles when appropriate if you have a blog or participate on forums of related topics. — SF






